Python最常用的函数、基础语句有哪些?

作者 | 朱卫军
来源 | Python大数据分析
一、内置函数
内置函数是python自带的函数方法,拿来就可以用,比方说zip、filter、isinstance等。
下面是Python官档给出的内置函数列表,相当的齐全。

下面几个是常见的内置函数:
1、enumerate(iterable,start=0)
seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
list(enumerate(seasons))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
list(enumerate(seasons, start=1))
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
2、zip(*iterables,strict=False)
>>> for item in zip([1, 2, 3], ['sugar', 'spice', 'everything nice']):
... print(item)
...
(1, 'sugar')
(2, 'spice')
(3, 'everything nice')
3、filter(function,iterable)
def is_even(x):
if x % 2 == 0:
return True
else:
return False
然后使用filter对某个列表进行筛选:
l1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
fl = filter(is_even, l1)
list(fl)
4、isinstance(object,classinfo)
「isinstance」是用来判断某一个变量或者是对象是不是属于某种类型的一个函数
如果参数object是classinfo的实例,或者object是classinfo类的子类的一个实例, 返回True。如果object不是一个给定类型的的对象, 则返回结果总是False
>>>a = 2
>>> isinstance (a,int)
True
>>> isinstance (a,str)
False
>>> isinstance (a,(str,int,list)) # 是元组中的一个返回 True
True
5、eval(expression[,globals[,locals]])
>>>x = 7
>>> eval( '3 * x' )
21
>>> eval('pow(2,2)')
4
>>> eval('2 + 2')
4
>>> n=81
>>> eval("n + 4")
85
常用句式
「1、format字符串格式化」
# 格式化字符串
print('{} {}'.format('hello','world'))
# 浮点数
float1 = 563.78453
print("{:5.2f}".format(float1))
「2、连接字符串」
string1 = "Linux"
string2 = "Hint"
joined_string = string1 + string2
print(joined_string)
「3、if...else条件语句」
# Assign a numeric value
number = 70
# Check the is more than 70 or not
if (number >= 70):
print("You have passed")
else:
print("You have not passed")
「4、for...in、while循环语句」
# Initialize the list
weekdays = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday","Wednesday", "Thursday","Friday", "Saturday"]
print("Seven Weekdays are:\n")
# Iterate the list using for loop
for day in range(len(weekdays)):
print(weekdays[day])
while循环
# Initialize counter
counter = 1
# Iterate the loop 5 times
while counter < 6:
# Print the counter value
print ("The current counter value: %d" % counter)
# Increment the counter
counter = counter + 1
「5、import导入其他脚本的功能」
# Initialize values
vacation1 = "Summer Vacation"
vacation2 = "Winter Vacation"
# Import another python script
import vacations as v
# Initialize the month list
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]
# Initial flag variable to print summer vacation one time
flag = 0
# Iterate the list using for loop
for month in months:
if month == "June" or month == "July":
if flag == 0:
print("Now",v.vacation1)
flag = 1
elif month == "December":
print("Now",v.vacation2)
else:
print("The current month is",month)
「6、列表推导式」
# Create a list of characters using list comprehension
char_list = [ char for char in "linuxhint" ]
print(char_list)
# Define a tuple of websites
websites = ("google.com","yahoo.com", "ask.com", "bing.com")
# Create a list from tuple using list comprehension
site_list = [ site for site in websites ]
print(site_list)
「7、读写文件」
#Assign the filename
filename = "languages.txt"
# Open file for writing
fileHandler = open(filename, "w")
# Add some text
fileHandler.write("Bash\n")
fileHandler.write("Python\n")
fileHandler.write("PHP\n")
# Close the file
fileHandler.close()
# Open file for reading
fileHandler = open(filename, "r")
# Read a file line by line
for line in fileHandler:
print(line)
# Close the file
fileHandler.close()
「8、切片和索引」
形如列表、字符串、元组等序列,都有切片和索引的需求,因为我们需要从中截取数据,所以这也是非常核心的技能。
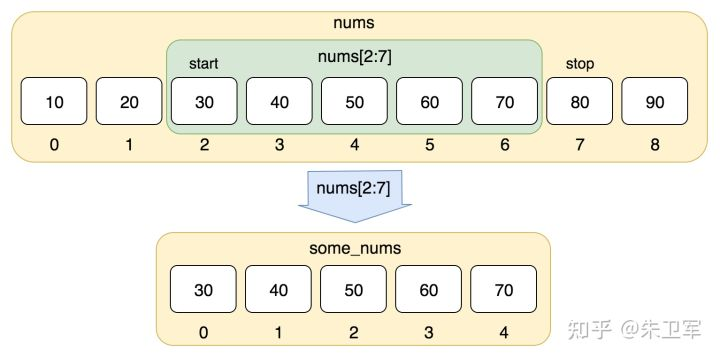
var1 = 'Hello World!'
var2 = "zhihu"
print ("var1[0]: ", var1[0])
print ("var2[1:5]: ", var2[1:5])
「9、使用函数和类」
# Define addition function
def addition(number1, number2):
result = number1 + number2
print("Addition result:",result)
# Define area function with return statement
def area(radius):
result = 3.14 * radius * radius
return result
# Call addition function
addition(400, 300)
# Call area function
print("Area of the circle is",area(4))
# Define the class
class Employee:
name = "Mostak Mahmud"
# Define the method
def details(self):
print("Post: Marketing Officer")
print("Department: Sales")
print("Salary: $1000")
# Create the employee object
emp = Employee()
# Print the class variable
print("Name:",emp.name)
# Call the class method
emp.details()
「10、错误异常处理」
# Try block
try:
# Take a number
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number % 2 == 0:
print("Number is even")
else:
print("Number is odd")
# Exception block
except (ValueError):
# Print error message
print("Enter a numeric value")
小结


分享

点收藏

点点赞

点在看
关注公众号:拾黑(shiheibook)了解更多
[广告]赞助链接:
四季很好,只要有你,文娱排行榜:https://www.yaopaiming.com/
让资讯触达的更精准有趣:https://www.0xu.cn/
 关注网络尖刀微信公众号
关注网络尖刀微信公众号随时掌握互联网精彩
赞助链接
排名
热点
搜索指数
- 1 中法友谊蕴山水 7904213
- 2 你以为的进口尖货 其实早已国产了 7808958
- 3 劲酒如何成了年轻女性的神仙水 7712208
- 4 盘点2025大国重器新突破 7615797
- 5 美国称将调整与中国经济关系 7522256
- 6 大雪吃三宝是指哪三宝 7425080
- 7 美军承认:击落美军战机 7330682
- 8 “两人挑一担 养活半栋楼” 7234390
- 9 中美合拍《我的哪吒与变形金刚》首播 7138827
- 10 周末去哪玩?雪场“不打烊” 7045319







 AI100
AI100







