Undertow URL解析特性及其安全风险分析
一、背景
在某次风险处理过程发现一处越权漏洞,攻击人员使用类似这样的请求访问到后台地址:
http://www.xxx.com/admin/..;/index.action
Web服务响应正常且返回了后台界面,而正确的请求应该是:
http://www.xxx.com/admin/index.action
近期再次发现一些未授权的漏洞利用连接中也有/..;/ 这样的特殊字符串,猜测可能是同一个原因导致,可能属于通用性的问题。
二、原理分析
2.1 正常请求
经过初步调查,业务环境使用的是Undertow+Springboot,Undertow是基于java nio的Web容器,等同于Tomcat,但是要比Tomcat更加轻量级。上述的漏洞利用链接格式与BlackHat 2018中Orange所提到一个Tomcat解析特性相似,相关文章。

Tomcat会将 /..;/ 这样的URL路径识别成根目录,而业务系统解析 /..;/ 这样的链接时可能会采取与tomcat完全不同的解析方式,比如上述文章提及的Nuxeo系统在进行鉴权时以 “;” 为分隔符,只对 “;” 之前的路径进行鉴权。代码如下所示:
protected static String getRequestedPage(HttpServletRequest httpRequest) {String requestURI = httpRequest.getRequestURI();String context = httpRequest.getContextPath() + '/';String requestedPage = requestURI.substring(context.length());int i = requestedPage.indexOf(';');return i == -1 ? requestedPage : requestedPage.substring(0, i);}
根据上述的逻辑,假设用户访问https://www.xxx.com/nuxeo/login.jsp;/..;/[unauthorized_area]
鉴权的时候分号之前是通过的,而访问的时候却是 unauthorized_area。为了确定URL的解析逻辑,下面通过测试和源码分析两个角度看一下实现过程。首先建立一个测试项目,定义两个FIlter文件(顺便看一下两种FIlter定义方式有何异同)、一个Config文件、一个Controller文件:
IndexFIlter.java
package com.undertow.filter;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.servlet.*;import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import java.io.IOException;@Componentpublic class IndexFilter implements Filter {@Overridepublic void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {System.out.println("过滤器被创建1");}@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest)servletRequest;StringBuffer path = httpRequest.getRequestURL();System.out.println("IndexFilter " + path);filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);}@Overridepublic void destroy() {System.out.println("过滤器被销毁1");}}
对于IndexFIlter通过FilterRegistrationBean的方式声明,FilterConfig.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configurationpublic class FilterConfig {@Autowiredprivate IndexFilter indexFilter;@Beanpublic FilterRegistrationBean registerIndexFilter() {FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean();registration.setFilter(indexFilter);registration.addUrlPatterns("*.action");registration.setName("indexFilter");return registration;}}
IndexFIlter2.java,直接通过WebFilter注解进行定义,这种方式要在启动类加上 @ServletComponentScan 注解
package com.undertow.filter;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.servlet.*;import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import java.io.IOException;@WebFilter(filterName = "IndexFilter2", urlPatterns = "*.action")public class IndexFilter2 implements Filter {@Overridepublic void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {System.out.println("过滤器被创建2");}@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest)servletRequest;StringBuffer path = httpRequest.getRequestURL();System.out.println("IndexFilter2 " + path);filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);}@Overridepublic void destroy() {System.out.println("过滤器被销毁2");}}
IndexController.java
package com.undertow.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class IndexController {@RequestMapping(value = "/index.action")public String index(){System.out.println("index");return "index";}}
运行,然后先执行一次正常的请求
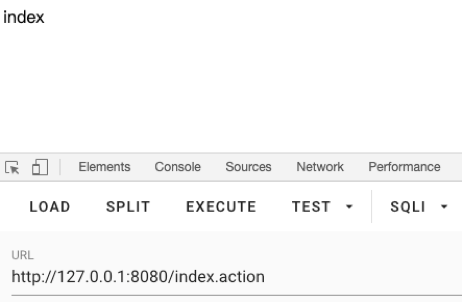
然后看请求日志
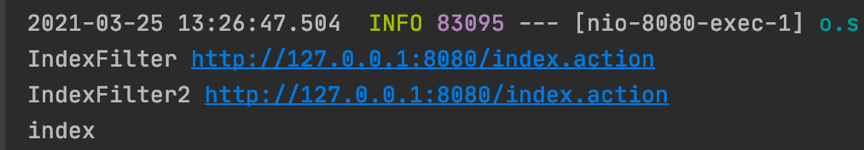 ?
?
两个FIlter都成功拦截到请求,并最终将请求转发到了Controller,以上是正常的请求,在Tomcat和Undertow中都执行正常。然后我们看一下当使用带有/..;/ 的异常连接进行请求的时候Tomcat和Undertow是如何执行的。
2.2 Tomcat 解析过程
在Tomcat中我们使用如下的异常链接进行一次请求
http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/..;/index.actio?
此时程序逻辑跟之前正常链接访问是一致的
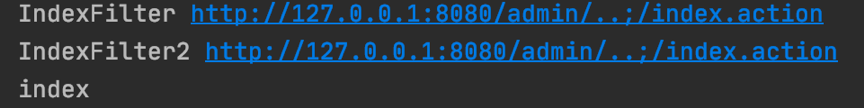
?
两个Filter成功拦截到了请求。为了进一步研究其中的原理,我们动态调试Tomcat解析过程,看一下源码是如何实现的。我们首先在 org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.java 中的 service 函数下断点,为什么在这里呢,因为此时 req 对象中的 URI 仍然是 /admin/..;/index.action 我们要看看它后续是如何变化的。
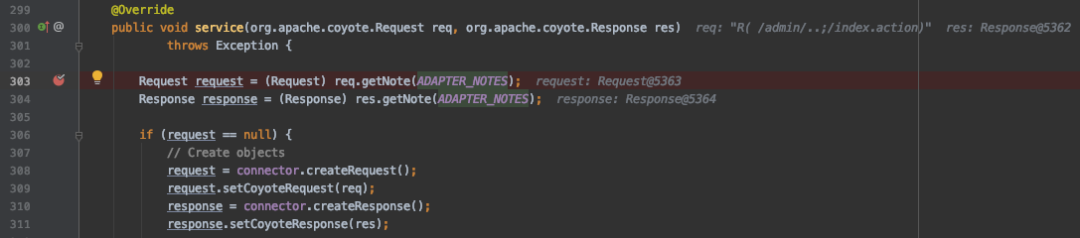
然后在337行跳转进入 org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.java 中的 postParseRequest 函数,根据函数介绍其作用就是对 request/response 进行必要的处理。我们重点看对URI的处理:
/**
Perform the necessary processing after the HTTP headers have been parsed
to enable the request/response pair to be passed to the start of the
container pipeline for processing.
*/
可以看到在601行和622行分别声明了两个变量,undecodedURI和decodedURI,前者是原始的URL的值,后者是解码的值(为空),然后625行将undecodedURI拷贝到decodedURI。
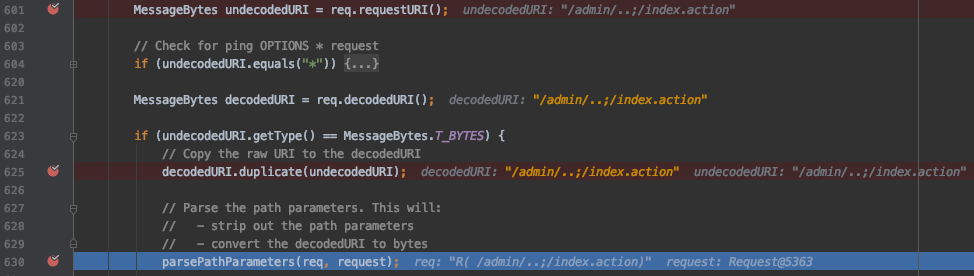
然后进入到 parsePathParameters 函数,这个函数是处理路径形如 /path;name=value;name2=value2 的请求,它定义了对分号的处理方式,图片中我折叠了部分代码,最终的处理结果就是删除了其中的分号,变成了这样的形式:/admin/../index.action
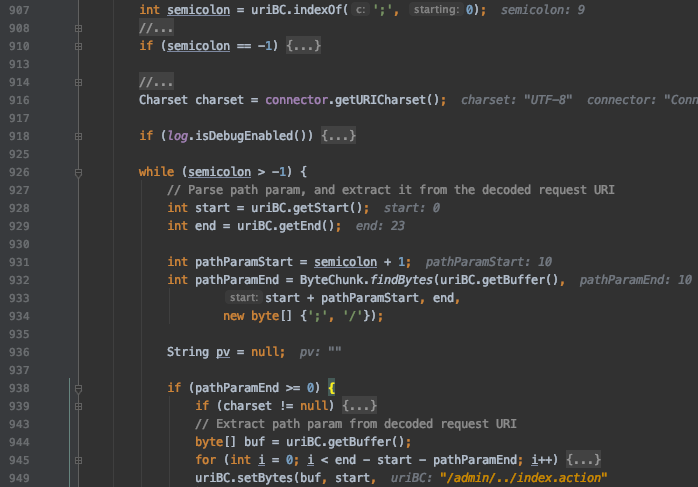
返回到 postParseRequest 函数后又进入到同文件的 normalize 函数,这个函数是对URI进行标准化
/**
?* This method normalizes "\", "//", "/./" and "/../".
?*/
经过上一步处理后,URI中有/../这样的关键字符,我们重点看下它是如何处理的
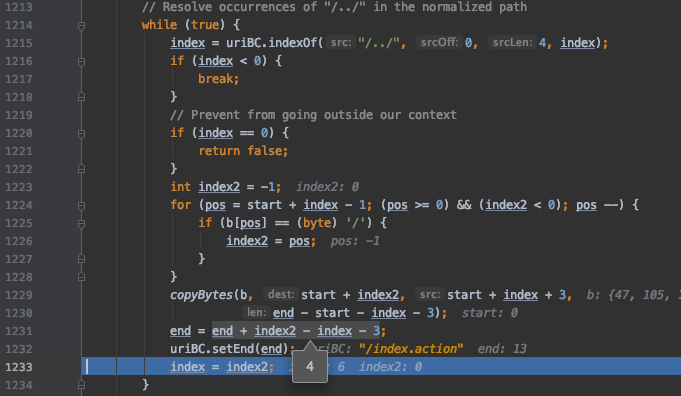 ?
?
其实过程很简单,以 /admin/../index.action 为例,代码先找到 /../ 的首字符位置,然后在此基础上加3,也就是 /../ 末尾字符的位置,然后将后面所有的字符前移,得到这样的字符:
/index.actionex.action
然后再根据 /../ 后面所有字符长度作为新字符串的长度,进行截断,得到最终的字符串,说白了就是删除 /../ 及其之前的字符串
/index.action
此时 decodedURI 的值就是 /index.action,undecodedURI 仍是 /admin/..;/index.action。然后在695行进入 org.apache.catalina.mapper.Mapper.java 中的 internalMapWrapper 函数,这个函数定义了7种URI映射规则,比如第一种精准匹配,第二种前缀匹配。它本质就是个URI映射器,决定了某个请求由哪个Servlet处理。
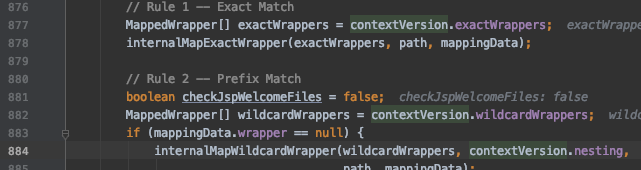
如果所有的规则都不匹配,则由最后的 Default servlet 处理。
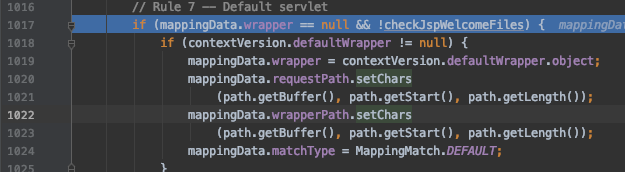 ?
?
这里相当于是解析 Controller 中定义的URI匹配规则,本示例代码中就是将 /index.action 请求解析到 IndexController。然后在 CoyoteAdapter.java 的343行程序经过多层调用进入 org.apache.catalina.ApplicationFilterFactory.java 中的 createFilterChain 函数,在103行的这个for循环里逐个检测请求的URI是否符合定义的 UrlPatterns。
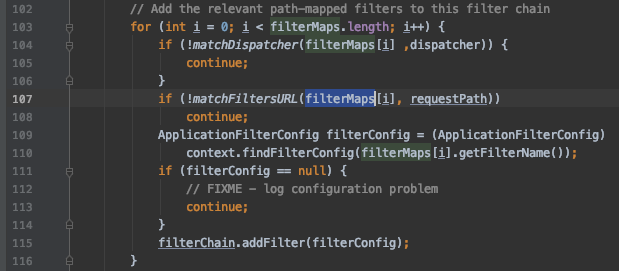
以上就是Tomcat解析URL以及的Controller和FIlter匹配URI的过程。
2.3 Undertow 解析过程
Undertow 需要显示的引用相关的包并排除tomcat:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId></dependency>?
然后在Undertow的环境下,使用2.2 节中Tomcat一样的异常链接进行一次请求,请求日志如下所示:
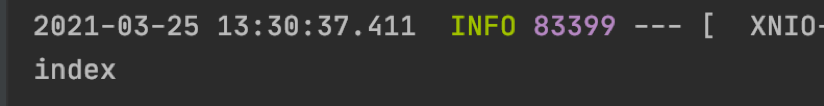 ?
?
我们发现Filter没有拦截到请求,但是 Controller 正确的执行了。再做一个测试,将 FilterConfig.java 的
registration.addUrlPatterns("*.action");
修改为
registration.addUrlPatterns("/admin/..");
然后再请求一次,后台日志如下所示
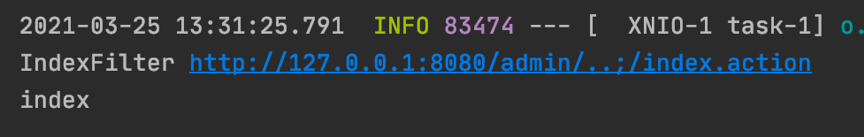 ?
?
可以看到IndexFilter 能拦截到,但是IndexFilter2 依旧不行,同样分析一下源码,Undertow URL 处理过程感觉要更绕一些,这里我们反向溯源,在 IndexController 中下断点,然后可以看到 RequestMapping 的匹配的是 "/index.action"

这个值来自于request变量
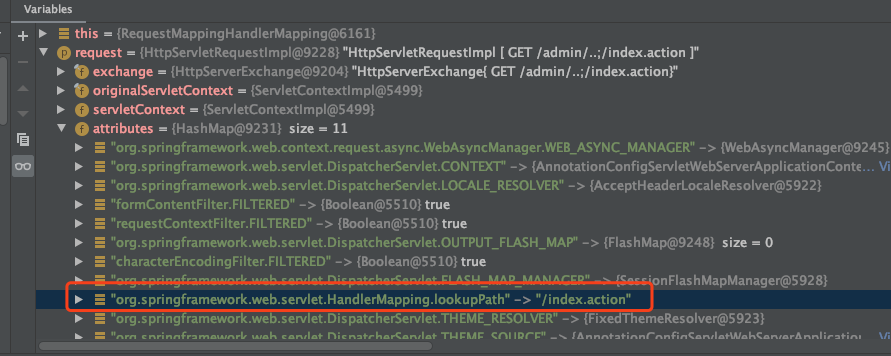 ?
?
在 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java 中的 getHandlerInternal 函数中将这个值放到 request 变量中
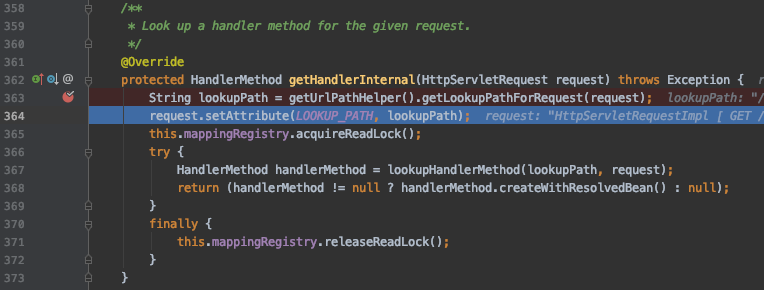 ?
?
然后看一下 lookupPath 是如何生成的,在 org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.java 中的 getPathWithinServletMapping 函数经过多次处理
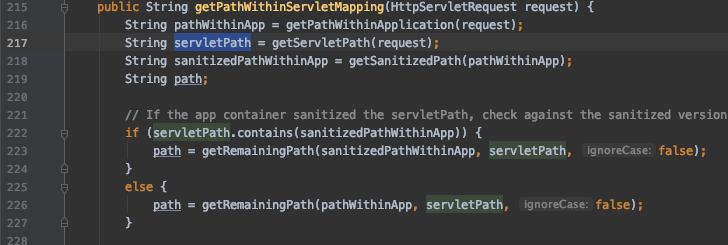 ?
?
首先在 org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.java 中的 decodeAndCleanUriString 函数对URI做清理,去除其中的分号
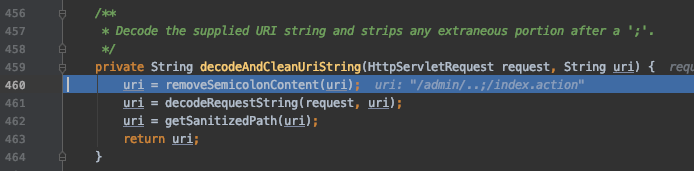
此时URI 变成 /admin/../index.action ,然后在同文件中的 getRemainingPath 函数中,将 mapping 尝试与 requestUri 进行匹配,若匹配成功,则返回剩余的字符串,这里 mapping 是 /admin/.. 那么剩余部分就是 /index.action
 ?
?
也就是说,当我们输入 /admin/..;/index.action 链接时,最终 Spring 进行路由匹配的路径是 /index.action。接着往下看,mapping的值是如何获得的,在 io.undertow.server.protocol.http.HttpRequestParser.java 中的 handlePath 函数中定义了处理步骤,412行以分号为分隔符,413行的servletRequestContext 函数将前半部分存储到 exchange 中,414行的 handlePathParameters 的函数将后半部分作为参数处理。

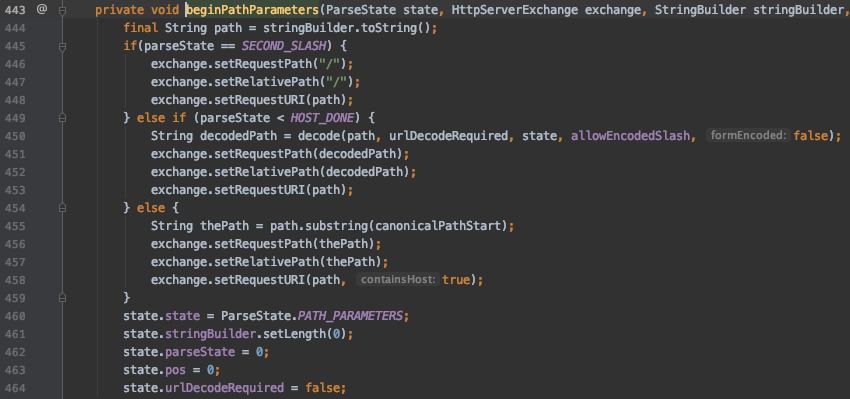
那么filter链是如何构造的呢?在 io.undertow.servlet.handlers.ServletInitialHandler.java 中的99行是分发请求的代码,
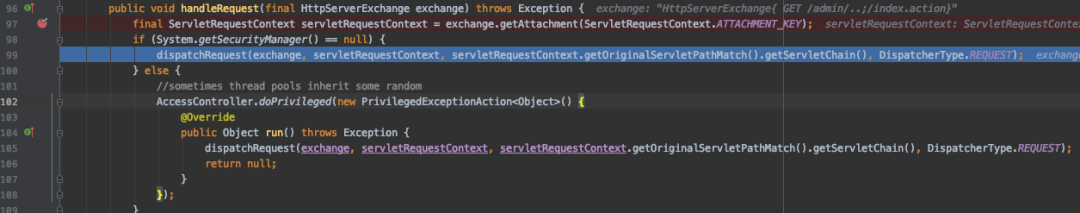 ?
?
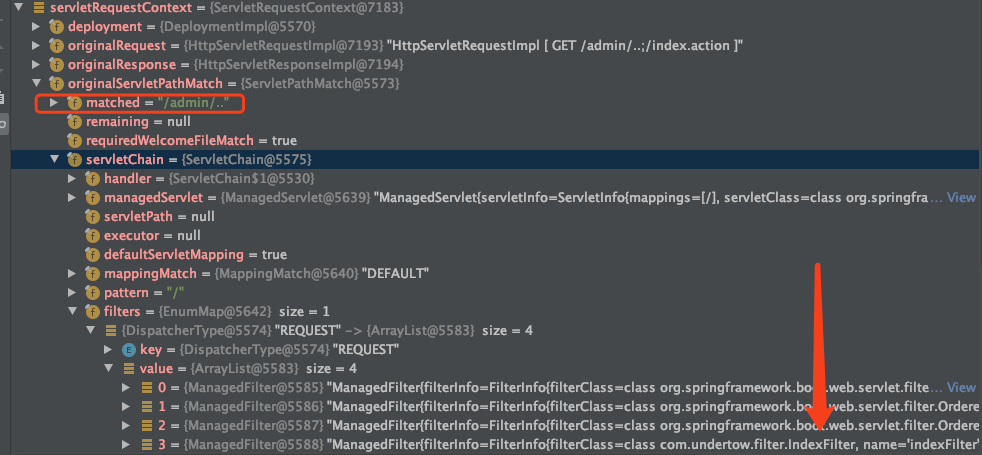
97行的 servletRequestContext 变量取自 exchange 变量,它已经保存了filter链,图中是将IndexFilter的URI匹配规则改为 "/admin/.." 后的结果。
2.4 结论
在使用Tomcat时,URL解析Filter和Controller是一致的,不存在歧义,如果自己的URL解析代码逻辑正确或者不自己解析就没有安全问题;在使用Undertow时,URL解析时如果遇到分号,容器会和框架会出现不一致,Filter解析分号前的URI,Controller解析分号后的URI,会在鉴权或恶意检测等场景出现绕过的风险。以
http://127.0.0.1/admin/..;/index.action
为例,当执行如下流程时可能会出现越权问题:
1、?在Filter中设置的鉴权逻辑,当检测到 *.action 且未登录时跳转到 /login.action
2、?在Controller中设置路由,当检测到 /index.action 时跳转到后台主页
3、?在Undertow环境下,Filter无法匹配分号前的 /admin/..,绕过鉴权的Filter,而Controller刚好匹配 /index.action,造成未授权访问
而这本质上不算一个漏洞,只是Web容器都有各自的解析特性,但使用不当可能会有安全问题。?
为了避免以上问题,在Undertow时,可以自行获取完整的请求路径进行鉴权。或者干脆对带有/**;/这样的请求进行全局检测,比如自行定义一个filter对类似的请求进行特殊的处理,可以去除异常字符也可以直接拒绝访问。
@WebFilter(filterName="Filter", urlPatterns="/**")
另外合理的使用spring security 也是一个不错的选择,测试发现spring-security 不仅能够有效进行访问控制,默认情况下还会对带分号的请求进行拦截:
The request was rejected because the URL contained a potentially malicious String ";"
?
三、参考文献
https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/181389.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/youzhibing/p/9866690.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65658315
百度安全应急响应中心
百度安全应急响应中心,简称BSRC,是百度致力于维护互联网健康生态环境,保障百度产品和业务线的信息安全,促进安全专家的合作与交流,而建立的漏洞收集以及应急响应平台。地址:https://bsrc.baidu.com


长按关注
关注公众号:拾黑(shiheibook)了解更多
[广告]赞助链接:
四季很好,只要有你,文娱排行榜:https://www.yaopaiming.com/
让资讯触达的更精准有趣:https://www.0xu.cn/
 关注网络尖刀微信公众号
关注网络尖刀微信公众号随时掌握互联网精彩
- 1 确保“十五五”开好局起好步 7904781
- 2 员工“踢了一脚” 救了老板一命 7809143
- 3 故宫下雪了 7712131
- 4 2026年经济工作要这么干 7616500
- 5 村支书卖小米被小米法务投诉下架 7523034
- 6 女子买千元羽绒服穿1天变吸油服 7424064
- 7 感觉时间越来越快不是错觉 7330871
- 8 不提“雪” 怎么描写雪很大 7232410
- 9 凭煮蛋涨粉350万 “蛋神”回应爆红 7141425
- 10 中央经济工作会议释放哪些重要信号 7043245







 百度安全应急响应中心
百度安全应急响应中心







